2 - Tier & - Tier Bicycle Rack
A bicycle rack is a structure designed to hold and secure bicycles when they are not in use. Bicycle racks are essential for providing organized parking in both public and private spaces and are commonly found in locations such as city streets, bike-sharing stations, public transportation hubs, parks, schools, universities and workplaces.
They are available in various configurations, ranging from simple and functional designs to advanced systems that maximize space efficiency or offer enhanced security features.
Types of Bicycle Racks.
- Standalone (Freestanding) Bicycle Racks.
- Wall-Mounted Bicycle Racks.
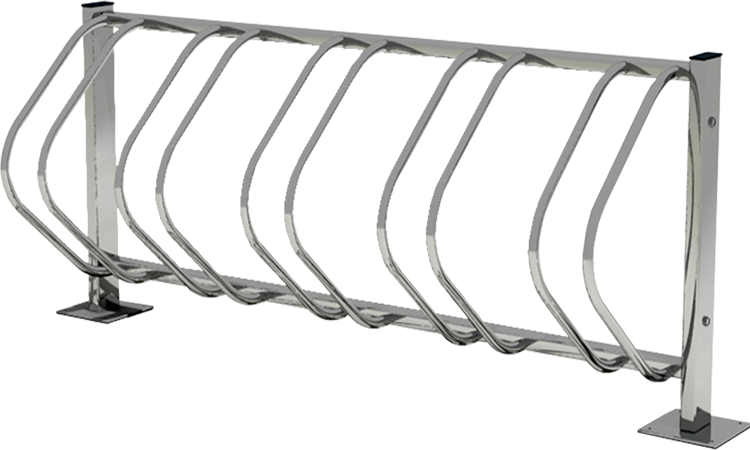
- Hoop (Ring) Racks.
- Post-and-Ring Bicycle Racks.
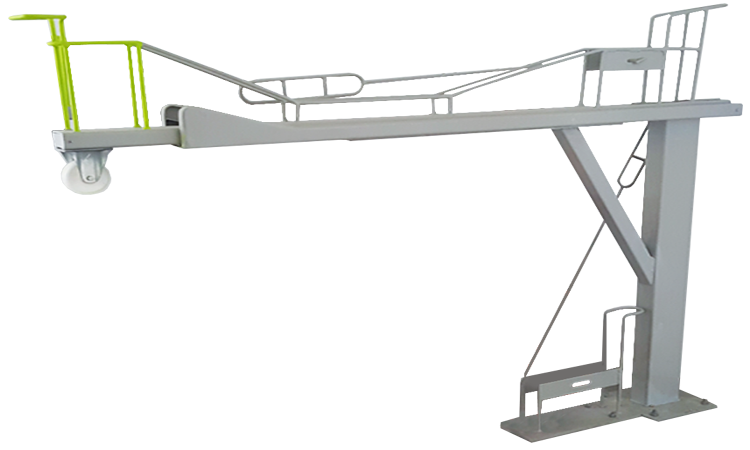
- Vertical (2-Tier / 3-Tier) Bicycle Racks.
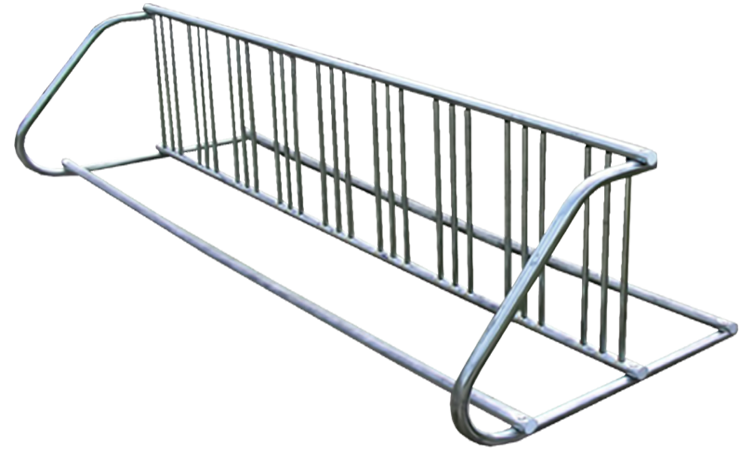
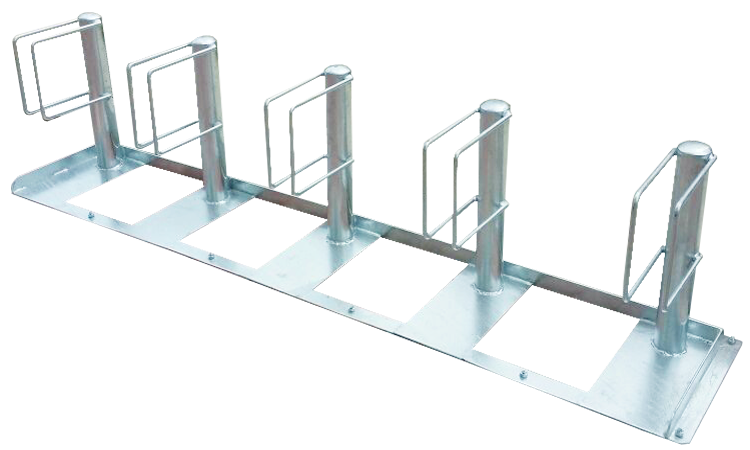
- Horizontal (Floor) Bicycle Racks.
- Locking Bicycle Racks.
- Bike Shelter Racks.
Design & Structure






Method of Installation
The production and installation of galvanized steel bicycle racks involve a combination of precise manufacturing, assembly and installation techniques. Galvanized steel is selected for its exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal material for outdoor
applications such as bicycle parking systems. Below is a step-by-step overview of the process used to manufacture and install galvanized steel bicycle racks..
Steps to Produce Galvanized Steel Bicycle Racks:
- Design the Rack:
- Concept: Determine whether the rack will be wall-mounted or freestanding, and select the appropriate type (e.g., hoop, post-and-ring, or grid-style) based on project requirements.
- Specifications: Define the dimensions, capacity and layout of the rack according to the site plan and usage needs..
- CAD Drawing: Develop a detailed 3D design using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to visualize the final product and make adjustments prior to fabrication.
- Material Preparation:
- Steel Selection: Choose the appropriate grade of steel, typically mild steel or cold-rolled steel, which will undergo the galvanizing process.
- Cutting to Size: Cut the steel into precise lengths for the rack frame using a bandsaw, plasma cutter, or laser cutter, depending on design complexity.
- Shaping and Bending:
- Bending: Form the steel tubing or rods into the desired shape using a tube bender or press brake. For complex geometries, CNC bending equipment may be used.
- Drilling Holes: Add mounting holes or attachment points using a drill press according to the design specifications.
- Welding: Join the components using MIG (Metal Inert Gas) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding techniques, depending on the required precision and finish quality.
- Galvanizing Process:
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: After fabrication, immerse the steel rack in a bath of molten zinc at approximately 450–460°C. The zinc chemically bonds with the steel, forming a long-lasting protective coating.
- Alternative: Electro-galvanizing can also be used, where a thin layer of zinc is applied through an electrochemical process; however, hot-dip galvanizing provides a thicker and more durable finish.
- Finishing:
- Inspection: Conduct a thorough quality inspection to ensure the galvanized coating and welds meet required standards.
- Additional Coatings: For enhanced protection and aesthetics, a powder coating layer can be applied over the galvanized surface. This not only adds color but also increases resistance to weathering and corrosion.
